How Can Surgical Microscopes Be Used In Stereotaxic Examinations?
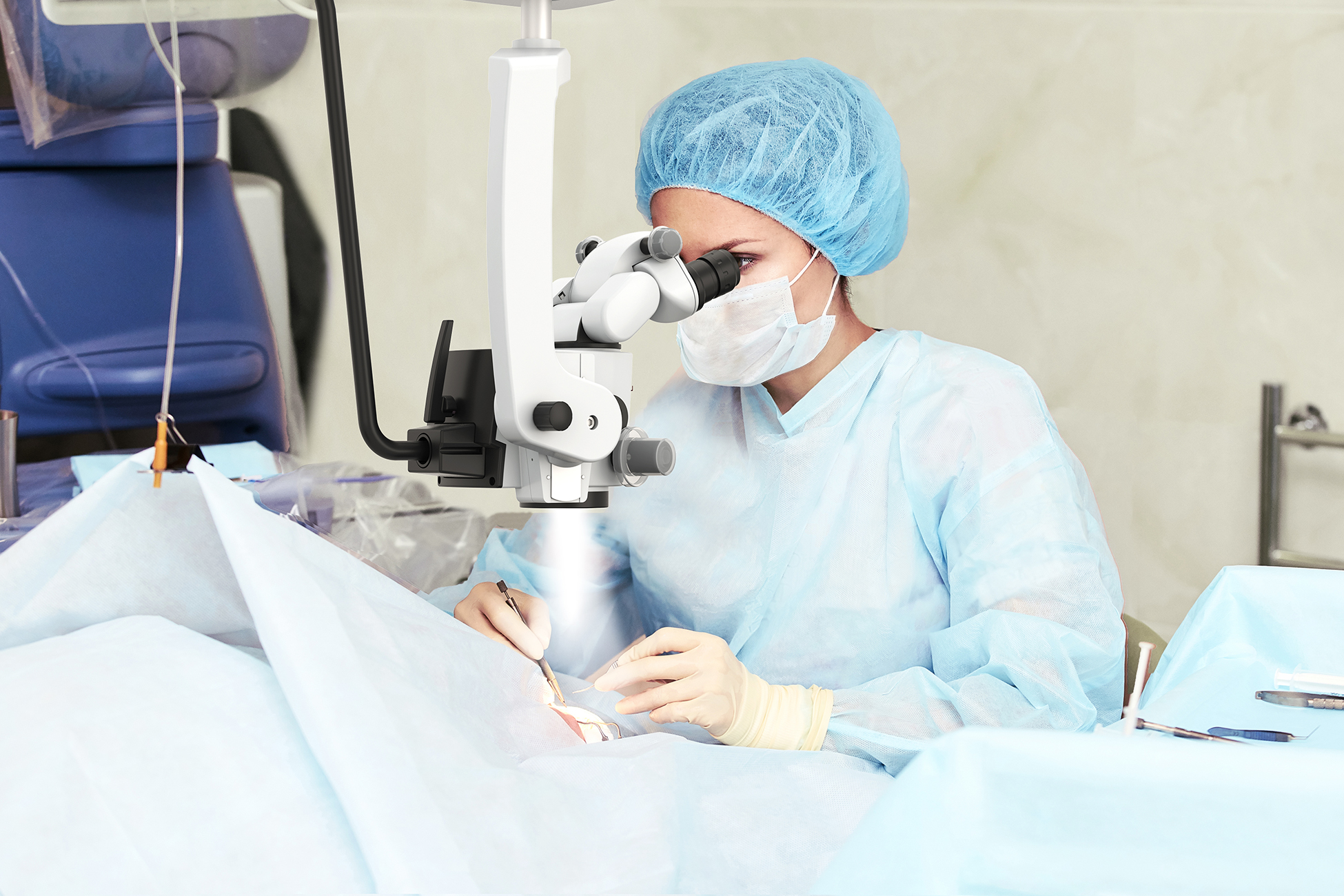
Understanding how can surgical microscopes be used in stereotaxic examinations is critical for researchers and clinicians who rely on extreme precision during neurological and preclinical procedures. In stereotaxic setups, where millimeter-level accuracy determines experimental success, surgical microscopes enhance visualization, depth perception, and procedural control. Their integration has become a cornerstone in modern stereotaxic surgery, especially in rodent neuroscience and translational research.
The role of surgical microscopes in stereotaxic procedures
Stereotaxic examinations involve navigating complex anatomical structures using three-dimensional coordinates. Whether performing microinjections, electrode implantation, or lesion studies, visibility and stability are non-negotiable.
Surgical microscopes support these requirements by offering:
- High optical magnification
- Enhanced depth perception
- Adjustable working distance
- Stable illumination without shadows
This combination allows researchers to operate with confidence while minimizing tissue trauma and procedural variability.
Stereotaxic surgery in mice
Stereotaxic surgery in mice is one of the most common applications where surgical microscopes prove indispensable. Mouse brains are small and highly sensitive, requiring exceptional visual clarity to identify landmarks such as bregma and lambda.
A surgical microscope allows:
- Accurate alignment of the stereotaxic frame
- Clear visualization of skull sutures
- Precise drilling and microinjection guidance
In advanced research, microscopes also assist in procedures like Stereotaxic Surgical Approach to Microinject the Caudal Brainstem and Upper Cervical Spinal Cord via the Cisterna Magna in Mice, where anatomical precision directly impacts survival rates and experimental reproducibility.
Stereotaxic surgery rat models
Compared to mice, Stereotaxic surgery rat models offer larger anatomical targets, but they still demand controlled magnification and stable visualization. Surgical microscopes help researchers maintain consistent viewing angles while working across longer procedures.
Key advantages include:
- Reduced operator fatigue during extended surgeries
- Improved identification of vascular structures
- Better coordination between manipulation tools and target sites
This is particularly valuable in behavioral neuroscience and pharmacological testing, where post-operative recovery quality influences study outcomes.
Stereotaxic surgery mouse protocol and visualization accuracy
A standardized Stereotaxic surgery mouse protocol often includes steps that benefit directly from microscope use:
- Animal positioning and leveling
- Skull exposure and cleaning
- Landmark identification
- Burr hole drilling
- Injection or implantation
At each stage, a surgical microscope enhances consistency and reduces the margin of error. By improving visual feedback, microscopes help ensure protocol adherence across different operators and experiments.
Optical advantages that support stereotaxic accuracy
Modern surgical microscopes are designed specifically for microsurgical workflows. Their optical systems play a direct role in stereotaxic accuracy.
Magnification and resolution
Variable magnification allows operators to zoom in during critical steps while maintaining broader situational awareness during setup.
Illumination control
Coaxial lighting eliminates shadows in deep surgical fields, ensuring consistent visibility of fine structures.
Ergonomics and stability
Binocular viewing reduces eye strain, while balanced arms and mounts keep the optical axis stable throughout the procedure.
These features align closely with findings from a Comprehensive review of surgical microscopes: technology development and medical applications, highlighting their growing importance in precision medicine.
Using a Microscope with a Stereotaxic Frame
Using a Microscope with a Stereotaxic Frame requires compatibility between optical systems and mechanical positioning devices. Surgical microscopes must offer sufficient clearance and adjustability to integrate seamlessly with the frame.
Important considerations include:
- Adequate working distance to accommodate instruments
- Flexible angle adjustment without repositioning the animal
- Stable mounts to prevent vibration transfer
When properly configured, the microscope becomes an extension of the stereotaxic system rather than a separate tool.
From stereotaxic surgery to stereotactic neurosurgery
While stereotaxic techniques are widely used in animal research, similar principles apply to Stereotactic neurosurgery in clinical environments. Surgical microscopes bridge the gap between preclinical experimentation and human application by enabling precise targeting of deep brain structures.
Emerging technologies such as Microscope-Based Augmented Reality in Degenerative Spine Surgery: Initial Experience further demonstrate how advanced visualization tools are shaping the future of image-guided interventions.
Training, reproducibility, and research quality
One often overlooked benefit of surgical microscopes in stereotaxic examinations is their role in training and reproducibility.
Microscopes help:
- Standardize visual reference points
- Improve inter-operator consistency
- Support documentation through imaging attachments
For laboratories onboarding new researchers, microscopes serve as a critical teaching aid, reinforcing best practices described in resources like the Beginner's Guide to Stereotaxic Surgery.
Limitations and considerations when selecting a surgical microscope
While surgical microscopes provide clear advantages, selecting the right system requires thoughtful evaluation.
Key factors include:
- Optical clarity versus digital enhancement
- Space constraints around stereotaxic frames
- Compatibility with imaging or recording systems
Choosing a microscope that aligns with experimental goals ensures long-term value and minimizes workflow disruptions.
Why surgical microscopes are essential in modern stereotaxic examinations
Revisiting How can surgical microscopes be used in stereotaxic examinations, their value lies in precision, safety, and reproducibility. As stereotaxic techniques become more sophisticated, the demand for advanced visualization continues to grow.
Surgical microscopes are no longer optional accessories, they are integral components of high-quality stereotaxic research and neurosurgical workflows.
Final thoughts: choosing the right solution for your lab
Whether working with Stereotaxic surgery in mice, Stereotaxic surgery rat models, or translational neurosurgical research, the right surgical microscope enhances accuracy at every step.
If your laboratory or institution is exploring reliable optical solutions, Labo offers contextual surgical microscope solutions designed for stereotaxic research environments, combining optical precision with ergonomic design to support consistent, high-quality outcomes.